Image/Video Retargetting by Anchor Point Sampling and Mapping
Fan Jiang and Jing XiaoAbstract
We proposes an efficient approach for image/video resizing while effectively preserving the important contents in the image/video. The approach consists of two major steps. First it computes the saliency of each pixel by combining a number of image features, and selects a small number of pixels, called anchor points, from the image/video by saliency-based sampling. It then determines the corresponding positions of these anchor point in the target image/video using efficient pixel mapping. Based on the mapping of neighboring anchor points, other pixels of the target are inpainted by back-projection and interpolation. The combination of sampling and mapping greatly reduces the computational cost yet leads to the globally sound solution to content-aware image/video resizing. Especially for video resizing, the reduced computational cost allows pursuing the mapping of pixels in the entire video altogether in one single optimization objective, which the previous methods can hardly do. Furthermore, to prevent disordering of pixel mapping, we propose an iterative adaptation algorithm. The performance of the proposed algorithms and comparison to existing methods are demonstrated.
Approach
| Image Example | Video Example | |
|---|---|---|
| 1) Original Image/Video |  |
 |
| 2) Saliency Map favoring human faces, edges, and motions |
 |
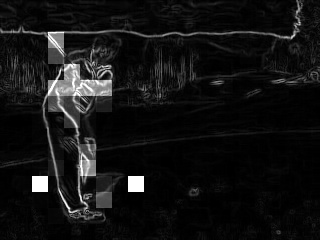 |
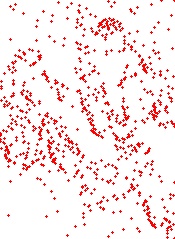
| 3) Anchor Point Selection favoring edges of the saliency map |
 |
 |
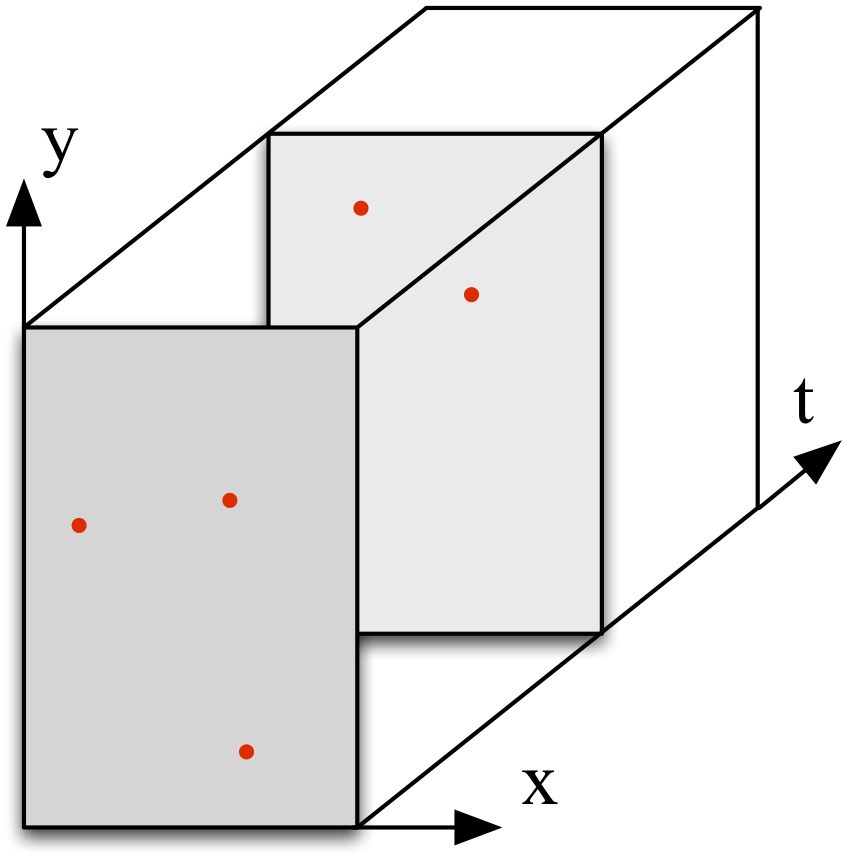
| 4) Anchor Point Triangulation 2D (image) or 3D (video) Delaunay triangulation |
 |
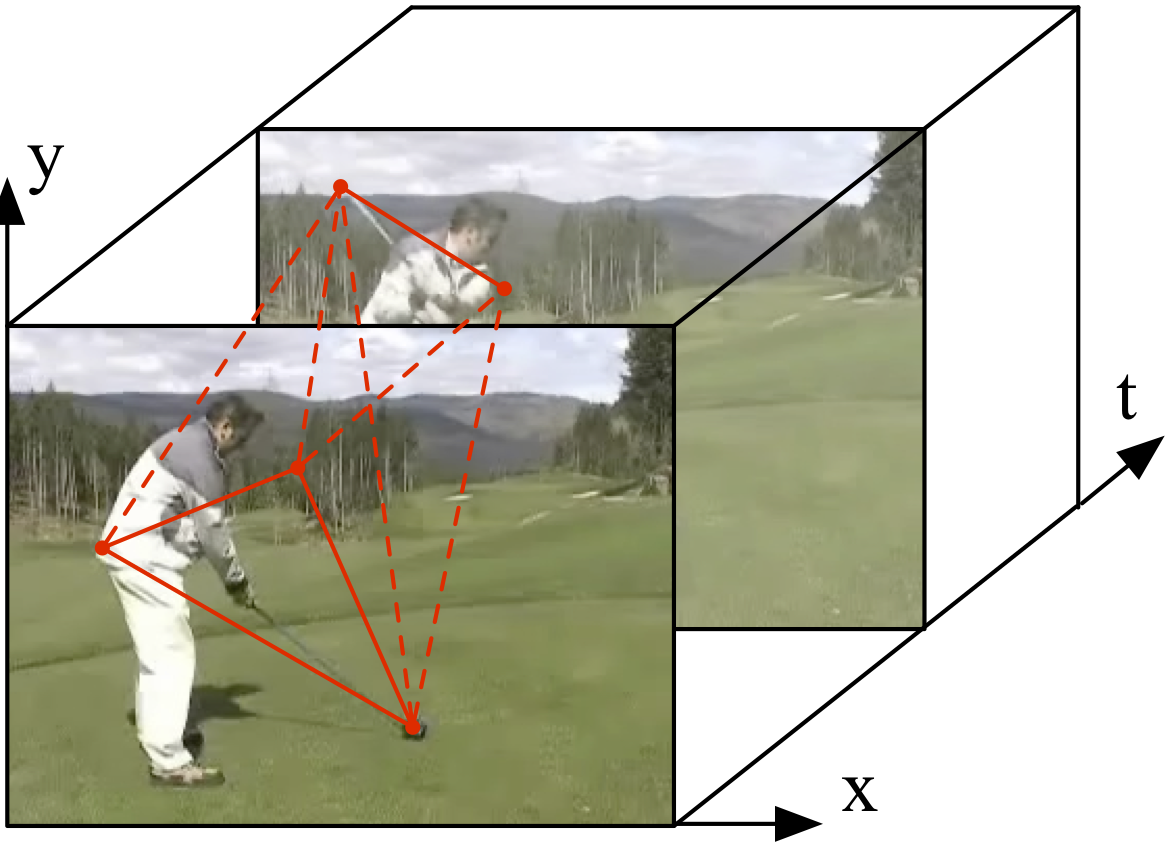 |
| 5) Anchor Point Mapping less resizing for salient regions more resizing for non-salient regions |
 |
 |
| 6) Retargetted Image/Video inpainting other pixels by back-projection |
 |
 |
Figure 1. Step by step illustration of the proposed resizing method.
Image Results
| Original | Enlarged | Shrinked |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Video Results
Press image to see video
 |
 |
| Original | Frame enlarged (compared to scaling) |
 |
 |
| Original | Frame shrinked (compared to scaling) |
 |
 |
 |
| Original | Frame enlarged + time shortened (compared to scaling) |
Frame shrinked + time expanded (compared to scaling) |
Patents
- Fan Jiang and Jing Xiao, "Effective and Efficient Content-Aware Image/Video Resizing by Anchor Point Sampling and Mapping," U.S. Provisional Patent Application Serial No.: 61/114,886, filed Nov 2008.